Accessibility Details
The site is designed in accordance with priority 1, 2, and 3 guidelines of the W3C Web Content Accessibility Guidelines and the Irish National Disability Authority Guidelines for Web Accessibility.
The web site has many accessibility facilities for disabled people and we intend to improve them and add to them over time. Accessibility features have been included for the following categories of disabled people.
Sight Impaired
- We have used large font as default, and used a lot of spacing between lines, and this facilitates easier reading for those people with slight visual impairment.
- We also have a facility for increasing the font size for those that have various visual impairments and may have trouble seeing or reading the text.
- There is a high contrast facility for visually impaired people with various backgrounds and text colours to make reading easier.
- There is a facility for audio reading of the text on a web page so that users can hear the text being read aloud with one simple click of the eSpeak button on each page.
- The eSpeak audio reading facility has text to inform the hearing impaired what it is.
- The alt tags describe content such as videos, audio, pictures, search buttons and form buttons for those using disability devices to view web content.
- Object tags have been made accessible
- Tables have been made accessible
- Iframes have title tags
- All forms are accessible
- The flash videos have a title and other markup to explain what they are
- The flash videos are accompanied by an explanatory audio for the visually impaired.
- Adobe PDF reader has some accessibility features built into it. We have provided a link to explanatory information about this beside all of our PDF file links on the site.
- The Search facility is on every web page, making it easy to access information onthe web site.
- The social networking and conferencing facilities have audio options and text options, and in the case of TeamTalk there are special accessibility options. There are also links to recommended conferencing software which have audio and text options. Disability devices can convert speech / data entry (via different methods) into text, and receive and process text messages or replies, thus facilitating communication in real-time for the visually impaired
Hearing Impaired
- A signage facility for the deaf and hearing impaired on each web page. This has been done using the latest version of Flash which has new accessibility features built into it to make it more accessible to disabled people. (See below). This section also has an audio description for the blind and sight impaired who cannot see flash videos.
- The eSpeak audio reading facility has text to inform the hearing impaired what it is.
- The videos on the web site have subtitles.
- The social networking and conferencing facilities have video options and text options, and in the case of TeamTalk there are special accessibility options. There are also links to recommended conferencing software which have video and text options. These facilities and software make it possible to video-conference and communicate via sign language over the Internet and also communicate via text blogging and chat.
Speech Impaired
- For the speech impaired we felt we needed text based blogs and chat section so that users can communicate with their friends and with NCPD in a safe and reliable manner. Some people with speech impairments also use sign language and the facilities for this are mentioned above in the ‘Hearing Impaired’ section.
Mobility Impaired
- There is a facility for tabbing through web pages and the web site. This facilitates the mobility impaired.
- The links to sections of a web site appear on the same screen, and are easy to see and access ; there is minimum scrolling / tabbing involved.
- There is also an audio reading of the text so that a person does not have to scroll down a page.
- The search button on each web page is in a prominent position, and it enables a person to type in what they want, click search and get the web page or information they require.
- There are also links to many important forms both on the website and on other web sites and this means a mobility impaired person does not have to travel any distance in order to get a form, fill out a form and post it.
Intellectually Impaired
- The layout of the web site is simple and straightforward, and it is easy to navigate and use. It is very difficult to get lost on the web site.
- An intuitive web interface
- Categorisation of information on each web page to make it easy to understand, access and use.
- Only relevant information is included on each web page and it does not include anything that is needless or unnecessary.
- The language used is plain language which is easy to understand
- There is an audio reading of the text, which enables a person to listen to the content of a web page being read out.
- The search button on each web page is in a prominent position, and it enables a person to type in what they want, click search and get the web page or information they require.
Other Accessibility Features
- The web site is readable in the different screen resolutions used by computers and disability devices
- Flash has new accessibility features. The following material has been sourced from the Adobe Flash website. Source: Adobe Flash website,
http://www.adobe.com/accessibility/products/flashplayer/overview.html
Adobe Flash Player 10 accessibility overview
With Adobe® Flash® Player 10, the best experience on the web is now even better.
With added support for scripting accessibility information, support for accessible components, enhanced integration with assistive technologies, and increased keyboard access, Flash Player 10 delivers a powerful new array of features. Together with Adobe Flash CS4 Professional software, Flash Player 10 offers developers the most robust set of tools available for developing accessible rich media. In addition, Flash CS4 Professional introduces new features that enable third-party developers to create a variety of extensions that make authoring and delivering accessible rich media even easier.
ENHANCED ACCESSIBILITY
With integrated support for Microsoft Active Accessibility (MSAA), Flash Player 10 makes content available via screen access technologies such as Window-Eyes from GW Micro, JAWS from Freedom Scientific, and NVDA from NVAccess. Flash Player 10 includes support for complex, dynamic sites that update their content via ActionScript. It also helps ensure that users with mobility impairments can move easily between content in the Flash ActiveX control and HTML content.
To help designers and developers ensure that rich Internet applications are accessible, Flash Player 10 and Flash CS4 Professional include support for updating and generating accessibility properties via ActionScript. This enables applications to update accessibility information as the content changes.
Additionally, the Accessibility Resource Center provides new documents offering tips and tricks to designers and developers seeking to create accessible Flash content. These documents include information on adding text equivalents to objects in Flash CS4 Professional, marking up forms, working with text, and adding animation. This site will be frequently updated with new tools and information to support accessible design in Flash CS4 Professional.
SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
To access Flash content using a screen reader, users need to have Flash Player 6 or later installed. Download the latest version of Flash Player.
Users also need a screen reader with the Flash Player implementation of MSAA. As Flash Player 10 is released, these include Window-Eyes from GW Micro, JAWS from Freedom Scientific, and NVDA from NVAccess. More information about the Window-Eyes, JAWS, and NVDA screen readers and demo versions for each are available on the GW Micro, Freedom Scientific, and NVDA Project websites.
Finally, screen reader users will need to access Flash content using the Microsoft Internet Explorer or Mozilla Firefox browsers.
ACCESSING FLASH CONTENT
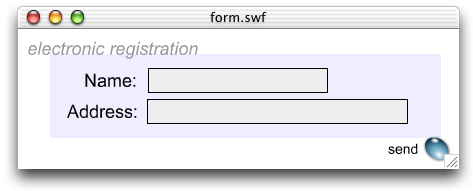
When a screen reader encounters Flash content, it typically announces the beginning and end of each FLV movie, SWF form, or other interactive content. Otherwise, the content functions the same way as HTML content on a web page. For example, the following SWF form contains four elements: the title, Electronic Registration; two input fields, Name and Address; and a Send button.
A screen reader would likely read this form as follows: "Electronic registration. Textfield Name. Textfield Address. Button send." The word "textfield" is a cue that a field needs to be completed. The word "button" is a cue that there is a button on the page. Screen reader users would complete these fields and activate the button in the same way they would in an HTML document.
An improvement made in Flash Player 8 and supported in Flash Player 10 makes it easier to assign a specific reading order for content using a screen reader. Authors now can specify values for only the relevant objects on the screen, instead of every object in the form. Flash Player reorders the objects into the desired reading order.
By default, Flash Player reads text elements, buttons, and input text in FLV and SWF content. Using Flash CS4 Professional, designers and developers can assign text equivalents for movie clips and even entire movies as well as forms.
With the new accessible components, designers and developers can easily create accessible web applications. Even the most complex movies and forms can be made accessible quickly and easily.
DOWNLOADING FLASH PLAYER 10
Before downloading Flash Player 10, assistive technology users need to use the HTML version of Adobe.com. Learn more about accessibility on Adobe.com.
To download Flash Player 10 from the HTML version of Adobe.com, choose Products from the main menu, select Adobe Flash Player 10, and click Download Now. You can also navigate directly to the Adobe Flash Player product area.
Source: Adobe Flash website, http://www.adobe.com/accessibility/products/flashplayer/overview.htm